Introduction
The use of Flange is widespread and highly significant in the industrial landscape. They serve as indispensable elements for the safe and efficient connection of pipelines, valves, pumps and other important components in numerous applications. In this article, we dive deep into the world of flanges, highlighting their importance, different types and standards, as well as their areas of application. Whether you already have sound technical knowledge or are a newcomer to this field, you will gain valuable and exciting insights.
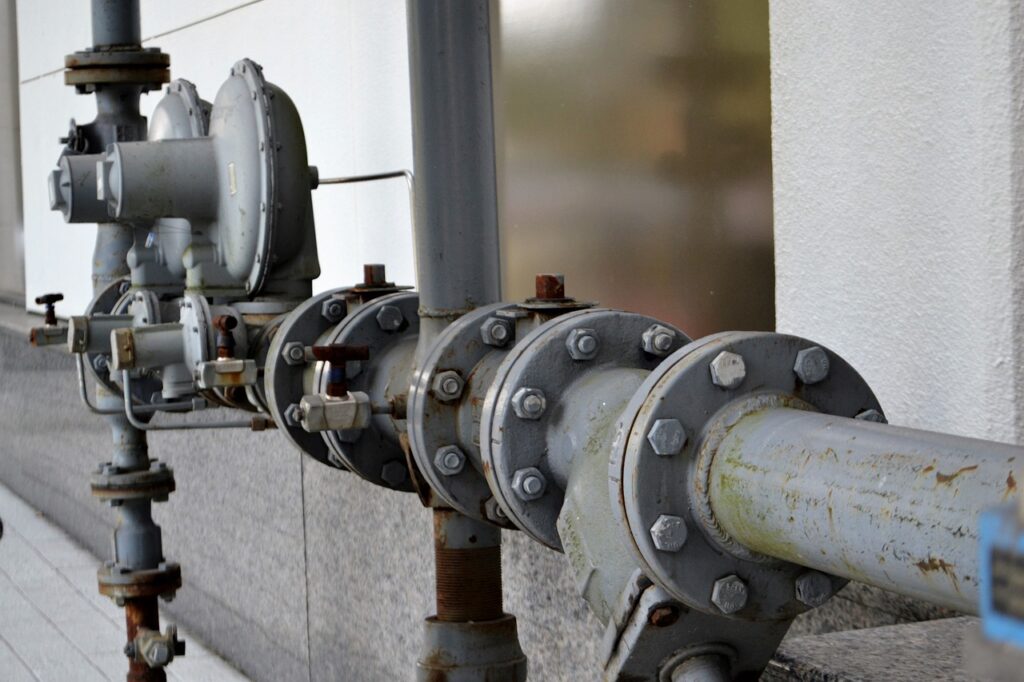

What are flanges? - A technical introduction
Flanges are among the essential components in the world of process engineering, plant engineering and supply engineering. They act as links between the various components of a piping system and enable a robust yet flexible connection. Essentially, a flange is a flat or slightly conical plate with holes through which screws or bolts can be inserted. Screwing the flanges together with special gaskets creates a leak-free connection.
Flanges can be made of different materials such as steel, stainless steel or plastic, depending on the requirements and operating conditions. The choice of material is of decisive importance, especially for high temperatures, pressures or corrosive media. It is therefore important to make precise considerations regarding material selection and flange dimensioning already in the planning phase.
But not all flanges are the same. There are different types of flanges, each with specific applications and uses. The most common types are the so-called flat flanges, blind flanges and welding neck flanges. While flat flanges are mainly used to connect pipes, blind flanges are used to close off a pipeline temporarily or permanently. Welding neck flanges, on the other hand, are often used in high-pressure applications.
In practice, flanges are often used in combination with other fasteners such as unions, couplings and gaskets. Choosing the right flange and associated fasteners is therefore a critical factor for the smooth operation of any industrial system.
In conclusion, flanges are an integral part of many industrial applications due to their versatility and importance in connecting system components securely and efficiently. Not only do they offer high mechanical strength, but they also allow for easy assembly and disassembly, making them an ideal choice for many engineers.
Different standards and types of flanges
In the world of flanges, there are a variety of standards that can vary depending on the application, geography and industry. The best known standards include the DIN-EN standards, the ANSI standards and the JIS standards. These standards define the specific requirements for dimensions, materials and tolerances that a flange must meet in order to be considered compliant with the standard.
An important aspect of selecting a flange is understanding the different types and their specific properties. For example, a distinction is made between flat flanges, welding neck flanges and blind flanges, to name but a few. Each of these flange types has its own areas of application and advantages as well as disadvantages:
- Flat flanges: Frequently used in low-pressure applications. They provide a good sealing effect and are easy to install.
- Weld neck flanges: Ideal for high pressure applications as they are welded directly to the pipe, creating an extremely stable connection.
- Blind flanges: These flanges are used to close pipe ends and are therefore important in installations and systems that could still be expanded.
It is essential to make the right choice, as the flange types have different installation and maintenance requirements. A blind flange, for example, allows for easier maintenance as it can be easily dismantled, while a weld neck flange requires a more permanent but also more complicated installation.
Furthermore, it is important to select the correct gasket materials and glands depending on the flange type and operating conditions. The wrong choice could lead to leaks or, in the worst case, to system failures.
In summary, knowledge of the various flange standards and types is an indispensable tool for engineers and technicians. It enables the optimal selection and application of these important fasteners in a wide range of industrial applications.
Detailed description of the different types of flanges and their applications
In this article we would like to give you an overview of three widely used flange types and highlight their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Weld neck flanges: The robust solution for high pressure applications

Weld neck flanges usually consist of a robust forging and are characterised by a long, conical hub. They are predestined for use in high pressure and high/low temperature applications. Their design minimises turbulence and pressure drops, preventing erosion and corrosion near the flange connections. There are two main variants: one for pipes and an extended type for process equipment.
Threaded flanges: The flexible option for low pressures
Threaded flanges are similar to the slip-on flange, but differ in having a tapered thread. This feature allows for easy attachment to pipes without the use of welding techniques. They are ideal for low pressure and temperature applications and are often used in water and air supply lines as well as in hazardous areas such as petrol stations and production facilities.
Blind flanges: The closing master in the pipe system
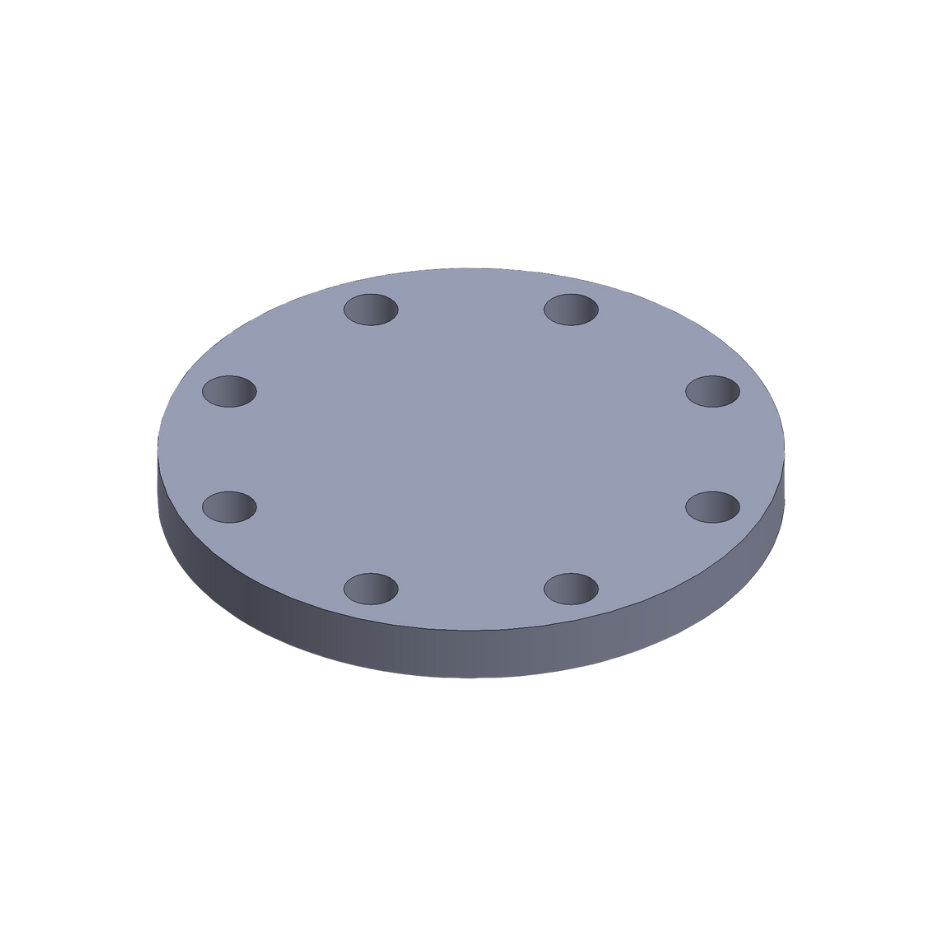
A blind flange has no central bore and is primarily used to close off piping systems. Due to its robust construction, it can withstand high mechanical loads caused by system pressure and bolting forces. Blind flanges also allow quick access to the pipe system, which facilitates maintenance and inspection. They are particularly suitable for testing the flow of gases and liquids in high-pressure applications.
Areas of application and importance in industry
The areas of application for flanges are diverse and extend across numerous branches of industry. They are used in the chemical industry, in mechanical engineering, in food processing and even in space travel. In the petrochemical industry, for example, flanges are indispensable for the safe transfer of liquids and gases under high pressures and temperatures. They act as critical connection points in complex piping systems and help to reduce leakage risks.
In the food and beverage industry, flanges have to meet special requirements, for example with regard to hygiene and material properties. Stainless steel flanges are often used here because they are corrosion-resistant and easy to clean. These properties are of particular importance in an area where compliance with strict hygienic standards is required.
Flanges also play a decisive role in energy supply. They enable the safe and efficient transfer of steam in power plants or of gas and oil in refineries. In such high-pressure environments, welding neck flanges and screwed flanges are particularly important, as they ensure a particularly strong and tight connection.
It is therefore not surprising that flanges are considered indispensable fasteners in modern industry. Their versatility combined with their high reliability makes them a first choice for engineers and technicians worldwide.
Flanges are not only functional components; they also contribute to economic efficiency and operational safety. By using standardised flanges, companies can save costs and increase the reliability of their plants at the same time.
In summary, flanges are an integral part of a wide range of industrial applications. They offer a robust, reliable and versatile solution for numerous connection tasks and are therefore an indispensable building block in the modern industrial world.
I hope this section meets your expectations. Now I will count the word count and keyword density for "flanges".
Constructive features
Flanges are amazingly versatile in their design. They can be equipped with a variety of thread types, sealing materials and bolting options. These design features offer a high degree of flexibility during installation and make maintenance much easier. Special designs, for example with sealing strips or sealing surfaces, can be selected depending on the requirements of the respective application. Furthermore, there are flanges with integrated measuring points or connections for sensors that enable continuous monitoring of the system. All these elements contribute to the fact that flanges are considered to be extremely adaptable and functional connecting elements.

Conclusion
The importance of Flange in modern industry can hardly be overestimated. They serve as indispensable connecting elements in a wide range of applications and contribute significantly to operational safety and efficiency. By choosing the right flange type and materials, engineers and technicians can maximise the performance and reliability of their equipment and systems. With constant advances in materials science and process engineering, flanges will continue to play a central role in industry.
Call-to-action
If you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your colleagues and professional circles. Your knowledge and experience can make a valuable contribution to the further development and application of these essential fasteners.
 CAD standard parts How to save 50% time - design quickly and easily
CAD standard parts How to save 50% time - design quickly and easily